Arthritis is a degenerative disease of cartilage tissue that can affect the vertebral joints and all bones of the skeleton.The hip joint (HJ) is the largest and most stressed bony joint.Therefore, coxarthrosis (arthrosis deformation of the hip joint) is a very common cause of disability among patients over 50 years of age.
Coxarthrosis (arthrosis of the hip joint): symptoms
Reason
The causes of coxarthrosis are varied.This pathology can lead to:
- Age-related dystrophic changes in cartilage.
- Continuous physical activity among athletes and carrying heavy loads for several years.
- Congenital dysplasia.
- TJ's injury.
- Necrosis of the femoral head (Perthes disease).
The head of the femur, covered with elastic cartilage, is located in the acetabulum of the pelvis.
There are unilateral lesions (when the disease affects one joint) and bilateral lesions - when both hip articular surfaces are affected.
Symptoms of arthrosis of the hip joint
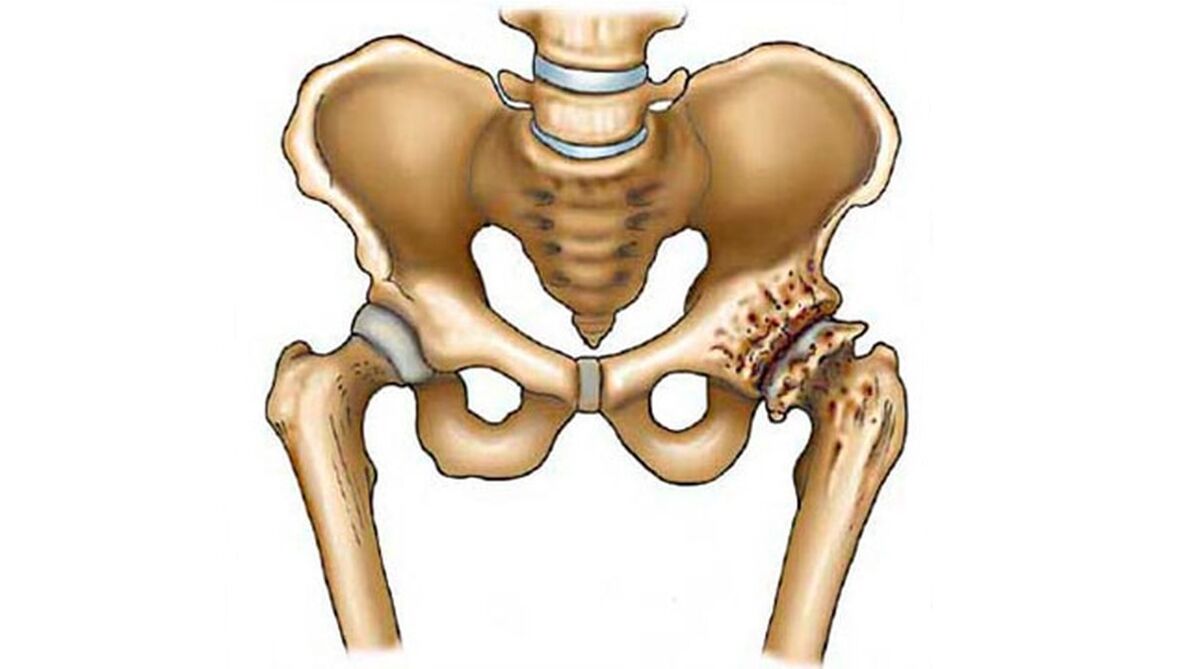
When diagnosed, the following symptoms of hip arthrosis are observed:
- Cartilage thinning, it becomes dry and rough.
- Thickening of the underlying bone, its growth to the side.
- Fibrotization and inflammation of the joint capsule.
- The appearance of inflammatory exudate in the capsule.
- Joint stiffness, contraction.
Externally, this change is shown by the following symptoms:
- Pain in the joints, radiating to the groin, hips and knees.
- Symptoms of pain begin (in the morning) that disappear after warming up.
- A stiff, uncertain, limping gait.
- By shortening the leg on the affected side (because this is a contraction).
- Femoral muscle weakness and atrophy.
- Deficiency in the joints.
Disease stage
Based on the signs and symptoms, three stages of the disease can be distinguished:
First
- Discomfort and pain, usually subside with rest.
- Absence of external symptoms - lameness, stiffness, atrophy.
Such signs are not particularly alarming patients, and few people pay attention to episodic pain, let alone start treating it.
But right at the initial stage, arthrosis of the hip joint is still a reversible disease.
Second degree
- Painful symptoms become more intense and can persist even at rest.
- Features of reduced hip function:
- Restriction of hip abduction and internal rotation appears
- defects are observed
- X-rays show:
- marginal osteophytes;
- deformation of the head and changes in its contour;
- Reduction of shared space.
Third Stage
- The pain became constant, and the most painful night pain also began.
- The patient had to rely on crutches.
- There is restriction of movement and atrophy of the gluteal, thigh and calf muscles.
- There is marked shortening of the legs and lameness.
- Due to excessive osteophytes, the joint space almost disappears, fusion and loss of function of the hip joint occurs.
It happens that the first attack occurs at a relatively young age - in the early forties.A person is most likely to forget about it and remember it at the age of 50-60 years, when deformations in the joints become important, affecting the quality of life.
Diagnostics
X-rays and functional diagnostics are carried out.Orthopedists not only decipher the image, but also rotate, bend the femur in all directions, and study the symptoms that arise when walking.
However, increasingly, if a patient is suspected of having coxarthrosis of the hip joint, leading experts refer to diagnostics using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).The explanation for this is the absolute safety and high information content of the procedure.It is an MRI examination that makes it possible to detect slight changes in the hip joint at an early stage, which contributes to the development of the most effective treatment tactics.
Treatment of coxarthrosis of the hip joint
Treatment is carried out according to the principle "the sooner the better."
Early coxarthrosis can be treated with:
- Chondroprotectors.
- Light physical therapy - swimming, aerobics, walking and cycling.
- Regulation of permissible physical load on joints.
- Weight correction (down).
- Physiotherapy treatment
- Extraction procedure.
- Massage session.
- Compress on the area of pain.
Painful symptoms can be relieved with NSAIDs.
Annual sanatorium treatment is also very effective.
Painful intra-articular corticosteroid injections can be used to treat more intense pain at a later stage.
Treatment of coxarthrosis in the final stage is very difficult due to the complete obliteration of the hip joint.Chondroprotectors in this case are useless.
All kinds of external drugs in the form of ointments and gels can relieve muscle spasms and pain, but, of course, will not affect the condition of immobile joints.Therefore, you need to take a sensible approach to all kinds of advertising that guarantees that by crushing the sore spot with ointment, you can forget about the disease.
Hip replacement
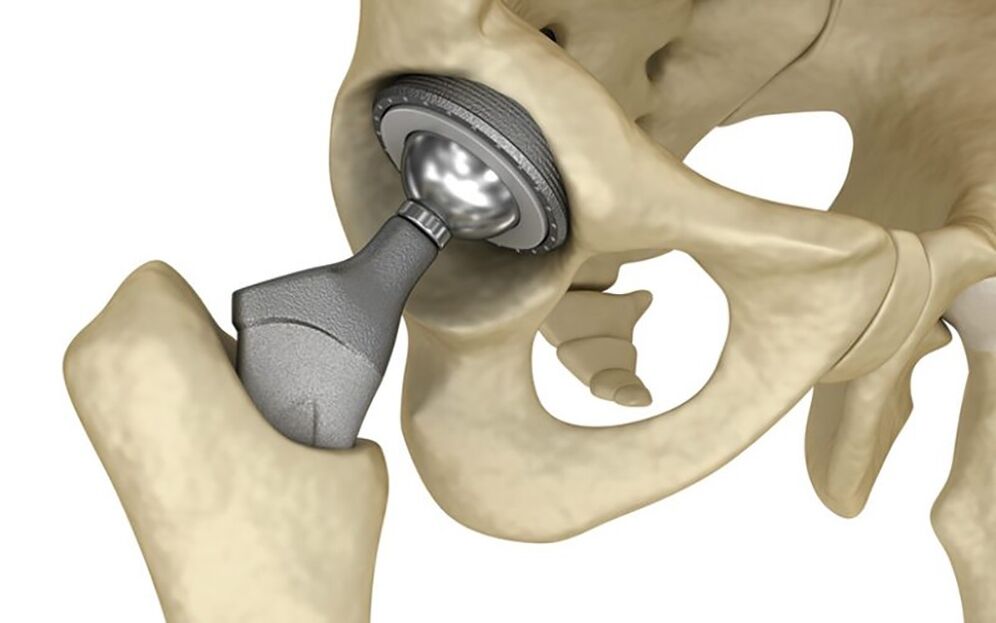
The only option for complete recovery of the hip joint in the third stage of coxarthrosis is surgery - endoprosthetics (artroplasty) of the hip joint.
Endoprosthesis consists of two components: head and cup.
This operation is not easy:
- After surgery, a long recovery period is required.
- Joint healing is painful (pain may persist for a year).
- You need to walk for some time with the help of a walker or use a cane as support.































